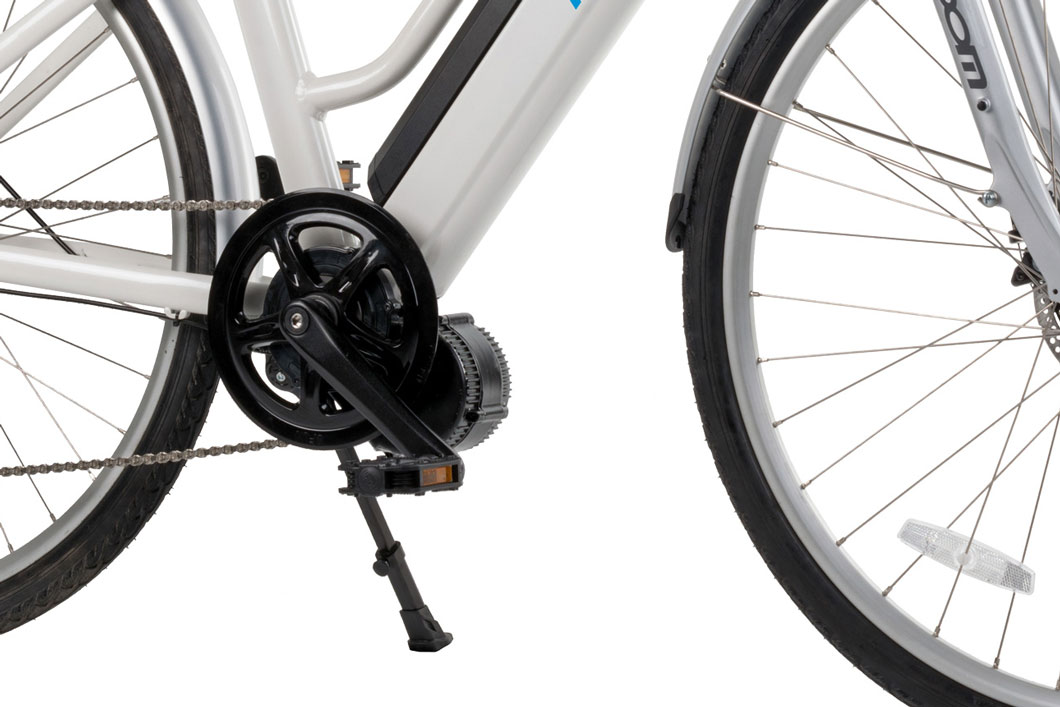
What is an e-bike?
E-bike is short for “electric bicycle”. E-bikes are simply bikes with electric motors built into their frames. These electric motors help propel e-bikes and their riders forward.
There are various types of e-bikes available worldwide. Some use a smaller motor to supplement the user’s pedal power. Other models with larger motors provide more energy, and essentially make the e-bike function like a moped, with no pedaling required.
E-bikes make mundane tasks like going shopping fun (and healthy).
Are e-bikes bicycles or scooters?
E-bikes are more bicycles than scooters. However, the use of an electric battery means that e-bikes can be classified as hybrid electric vehicles. Their electric motors combine battery power with the rider’s pedal-power.
E-bikes are more different from motorcycles and mopeds. Legally, e-bikes are still classified as bikes in most states. Laws regulating the usage of heavier vehicles don’t apply to e-bikes.
However, due to their increasing popularity, regulations specific to e-bikes have also been introduced in some countries, such as the US and Australia. These include the introduction of speed limits and the maximum amount of power generated by the motor.
How do electric bikes work?
Put simply, an electric bike combines the energy of an electric motor with the energy of a rider’s pedaling. This allows the rider to ride the bike at greater speeds than a regular bike, all while using less effort.
There are two types of eBike motors, and their difference is based less on performance and more on practicality.

Pedaling is one way to get going fast on an electric bike.
Pedelec Motors
E-bikes with motors in the middle are known as pedelec motors. These models are typically more expensive, and look more like a regular bicycle. Pedelec motors are generally smaller in size, and require more pedaling.
Hub Motors
E-bikes with motors on the wheel hubs are cheaper, and operate better under challenging road conditions.
The main difference between pedelec and hub motors is that pedelecs regulate their motor by pedaling. In contrast, e-bikes with wheel hub motors typically feature a throttle to control the speed and power.
E-bikes supply power from their motor in two ways.
The first way is through a traditional throttle-based delivery system, similar to an actual motorcycle. The other way is via pedal assistance. Of the two, pedal assistance is seen as the superior choice, as its power delivery system leads to longer battery life.
Types of e-bike batteries
There are two main types of eBike batteries.
1. Externally Mounted Batteries
Externally mounted batteries are heavy and can make riding a bit more intense. However, they come with the convenience of being easy to replace and recharge.
2. Integrated Batteries
Integrated batteries are lighter and produce less heat than their externally mounted counterpart. This comes with the tradeoff that if the battery runs out, it must be charged near a power outlet before the bike can be used again correctly.
An average e-bike rider can expect the battery to cover around 100-120 km on a single charge. However, it depends on the battery. Some batteries are closer to 50-60 km per charge, and others are upward of 400 km.
How fast can e-bikes go?

The fastest dog can run 20 miles per hour. Ebikes are faster.
Since an e-bike is still a bicycle, it can essentially go as fast as you can pedal it. In terms of assistance from the motor, most e-bikes stop providing electric propulsion if you exceed 32 km/h.
Some high-end models can provide assistance that allows your bike to reach speeds of about 45km/h!
What Laws Apply to e-bikes?
Due to the increasing popularity of e-bikes, new laws and regulations have been introduced to deal specifically with this type of hybrid vehicle.
Countries around the world have revised their existing laws and policies to regulate the use of e-bikes effectively. For example, the UK and other European countries follow these standards:
- An eBike must be fitted with a motor with a power of no more than 250w.
- It must provide a maximum assisted speed (i.e., the speed at which motor assistance is automatically cut off) of no more than 25 km/h.
- It must not be fitted with a full-speed throttle that can work ‘independently’ (that is without the pedals ‘moving forward’). Start-Up Assist throttles (those that assist up to 6 km/h) are allowed.
- It can be ridden without any minimum age limit.
These standards can be different from those being followed in other countries, such as Australia or the US.
Further legal differences and standards can also come into play at lower levels of government. For instance, different US states have different user requirements. The maximum speed for an eBike in Arizona is 20 mph, while in Idaho, the maximum speed is 30 mph.
Should I Get an e-bike?
There are many benefits to purchasing and riding an e-bike. For example, if you choose to commute to work on an e-bike, you can save money on fuel and other travel costs. Another advantage is that you reduce your carbon footprint by opting for a bike instead of a gas-powered vehicle.
Since e-bikes also function as traditional bicycles, you can also get some exercise while traveling to your destination. E-bikes enable you to live a healthier lifestyle overall.
Ultimately, you must decide whether purchasing an e-bike is the best decision for you. If you’re ready to take a look at some starter e-bikes, Keego has a growing range of affordable and high-quality city e-bikes for you to check out.



